Caring for sick patients isn’t just about providing the best in medical care; it’s also about ensuring a safe and sanitary environment. In today’s post, we’ll be discussing how hospitals can effectively and safely manage biohazardous and medical waste. Don’t let the intimidating and potentially dangerous task of waste disposal stop you from giving your patients the best possible care—follow these tips to help you navigate the minefield of biohazardous waste management!
Sources of Biohazardous and Medical Waste

They come in many forms and can originate from a variety of sources. For example, human body fluids such as blood and marrow, as well as surgically removed tissues, organics and instruments, present an immediate need for proper separations, containment, packaging and processing prior to disposal. Other examples include laboratory cultures and stocks of infectious agents or their associated toxins or any other material that may pose a risk of contamination to facilities personnel and the environment.
It is important for facilities to recognize the types they generate in order to ensure that appropriate processes are in place for medical waste management. Some common categories of sources include:
- Patient care: discarded surgical materials or equipment used during physical examinations; discarded pharmaceuticals; biological specimens; discards from operating rooms; laboratory materials used for diagnostics; discards from intensive care units
- Laboratory settings: cultures and stocks of infectious agents including test tube cultures, laboratory research material such as animal carcasses or parts contaminated with potentially infectious organisms
- Research programs: specimens collected through animal experimentation including tissue samples or organs excreted by animals following surgery
- Environmental sources: generated as a byproduct of environmental sampling activities designed to identify potential contaminants in the environment such as soil samples containing pathogenic organisms.
Proper Disposal of Biohazardous and Medical Waste
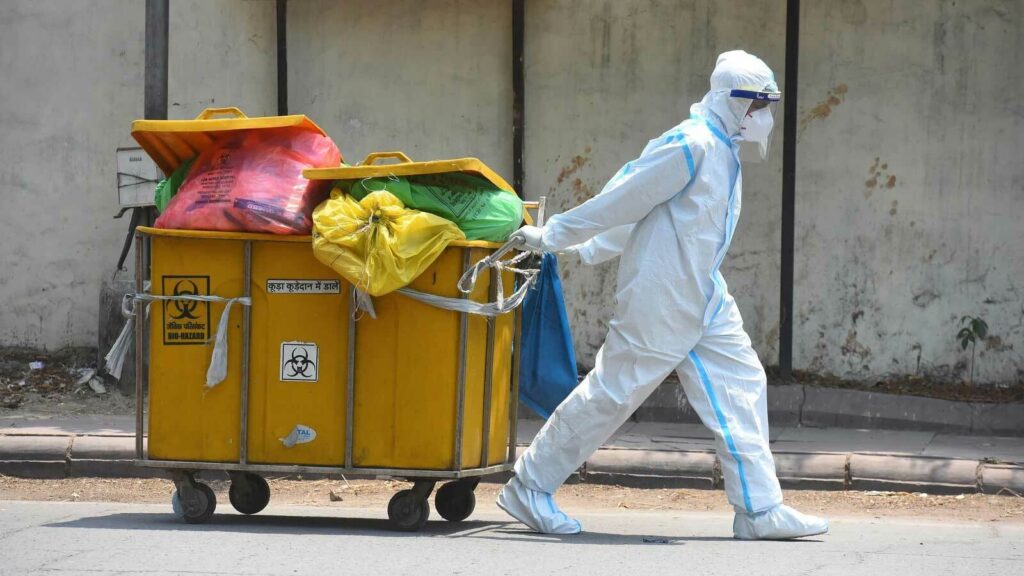

Proper disposal of them is essential for preventing the spread of infection and disease. All hospitals, clinics, and healthcare facilities must adhere to regulations set by the local or federal governments for handling and disposing of potentially infectious material. In order to ensure that biohazardous and medical waste is properly contained, handled, stored, transported, and disposed of, healthcare facilities need an effective waste management program.
When creating a waste management program for disposal of medical waste, it is important to consider these key points:
- Segregation: Healthcare facilities should segregate their medical waste into categories such as human tissue/fluids (including sharp objects), pathology/biological laboratory materials (such as cultures), pharmaceuticals (tablets or capsules), radioactive materials (radioactive isotopes), etc.
- Collection receptacles: Collection receptacles should be used in patient care areas in order to properly contain medical wastes until they can be removed from the facility.
- Labeling & Identification: Containers must be labeled and clearly identified as containing biohazardous material—in accordance with any applicable federal or state laws—so that individuals who come into contact with them know the appropriate safety protocol when disposal procedures are being followed.
- Storage & Transportation: Proper storage and transportation conditions must be established within the garbage facility in order to ensure all biohazardous materials remain contained during handling, moving from one place to another. Automated loading systems or dedicated vehicles may also be necessary depending on a facility’s size and type of equipment being used for transport.
- Final Disposal: Biohazardous/medical wastes should only be disposed at approved off site locations after all necessary steps have been taken to ensure proper containment and safety procedures have been followed correctly; this includes providing proof that the location has been adequately cleaned up before transport leaves the premises.
Benefits of Properly Managing Biohazardous and Medical Waste

Regulatory compliance and patient safety are two of the most important considerations in any healthcare environment. Properly managing biohazardous and medical waste is essential to ensuring these two components are maintained. Additionally, the proper management of biohazardous and medical waste can provide numerous benefits that can help optimize operations, preserve resources and reduce costs for hospitals.
Some key advantages to properly managing biohazardous and medical waste include:
- Reduced environmental impact: Reducing the amount of waste sent to landfills helps lower the environmental effect of hazardous materials on the surrounding environment. It cuts down on risks associated with disposing materials incorrectly by reducing contamination incidents and leaks caused by improper disposal.
- Enhanced patient safety: Working with specialized vendors or subcontractors who employ certified professionals reduces risk in handling potentially infectious materials, thus improving overall safety for patients, staff, and visitors inside the hospital itself.
- Lower operational costs: When hospitals partner with trained infectious material removal specialists they can save money by reducing labor hours required for collecting hazardous material or disposing it properly in a legal manner. This also reduces overtime labor costs associated with running an internal procedure to manage those same duties.
Regulations and Guidelines for Managing Biohazardous and Medical Waste
They must be managed in a way that meets certain guidelines, regulations, and standards. Hospitals that generate this type of waste must follow the laws set out by their state, as well as those set out by federal organizations such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), Department of Transportation (DOT), and Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). Following these guidelines helps to ensure safety for healthcare workers, patients, visitors, and the environment.
In addition to following federal guidelines, it’s important for hospitals to also stay up to date on any state-specific requirements or restrictions related to managing this type of waste. It’s also important for hospitals to develop their own internal policies and procedures that are in accordance with all regulations so that everyone is aware of how to safely handle potentially dangerous material:
- Stay up to date on any state-specific requirements or restrictions.
- Develop internal policies and procedures in accordance with all regulations.
- Use appropriate safety measures such as protective clothing when handling biohazardous materials.
Conclusion
In conclusion, effective management of it is paramount for any healthcare facility in order to provide a safe work environment for staff and protect the public from potential exposure hazards. Through appropriate containment before disposal or treatment in accordance with all applicable regulations, you can ensure proper handling at every stage while adhering to best practices with regards to safety compliance.




